Blockchain Basics: Breakdown of Top 6 Concepts for Beginners

Blockchain solves some major problems of the digital age. It’s key to cryptocurrencies, DeFi applications, NFTs, and smart contracts.
Blockchain is a modern technology that provides secure transactions, reduces compliance costs, and speeds up data transfers. Just to emphasize how much this technology is growing, here’s an interesting fact. According to MarketsandMarkets, the global blockchain market in 2022 was around and by 2027, it is set to generate revenue of over $94.
While the fundamental blockchain concepts are complex, this guide provides a simplified breakdown crucial to understanding blockchain.
What is Blockchain
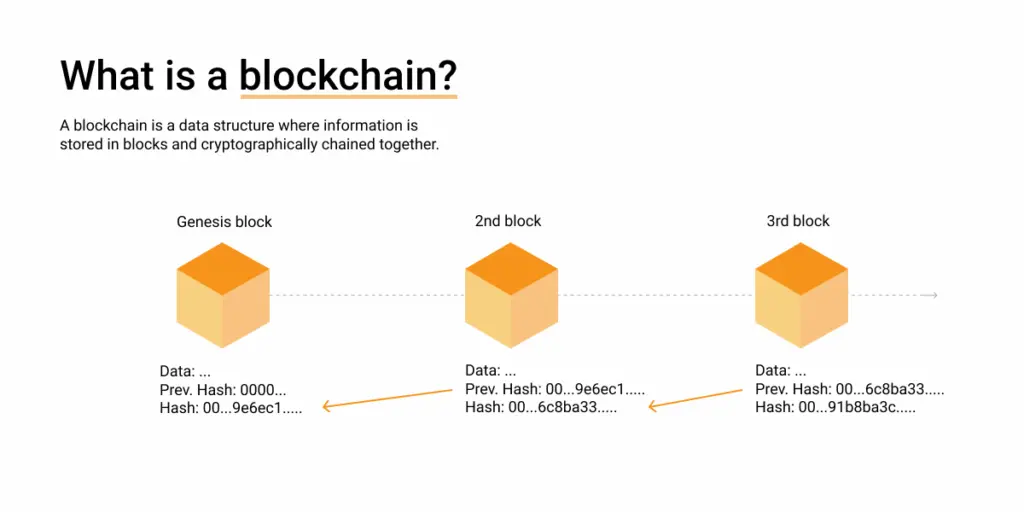
Photo: What is blockchain?, Source: opennode.com
Blockchain is a distributed database or ledger shared among a computer network's nodes. Basically, it facilitates the process of recording transactions and tracking assets in a business network. It can also disable data alternation.
People from all parts of the world can collectively maintain a database without relying on a central authority.
Basic Blockchain Concepts
Here are some of the most key concepts you should understand to safely navigate the Web3 space.
1. Decentralization
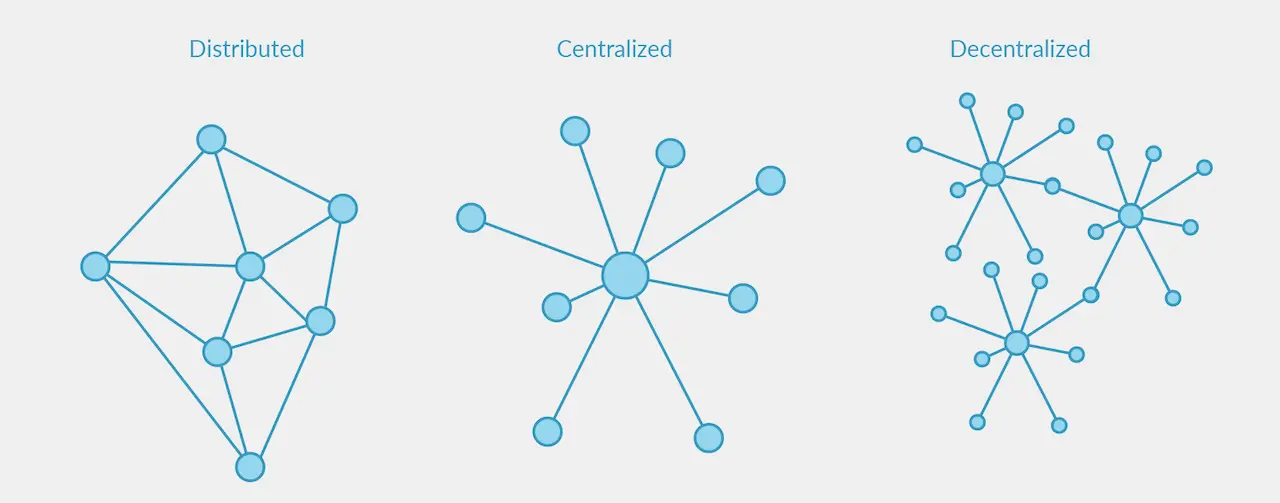
Photo: Centralized vs Decentralized system, plesk.com
The traditional systems are centralized. There’s a single entity that controls data and operations.
On the other hand, blockchain is a decentralized network of nodes. Each node stores a copy of the entire blockchain. There is no single point of failure which ensures transparency and security.
2. Consensus Mechanisms
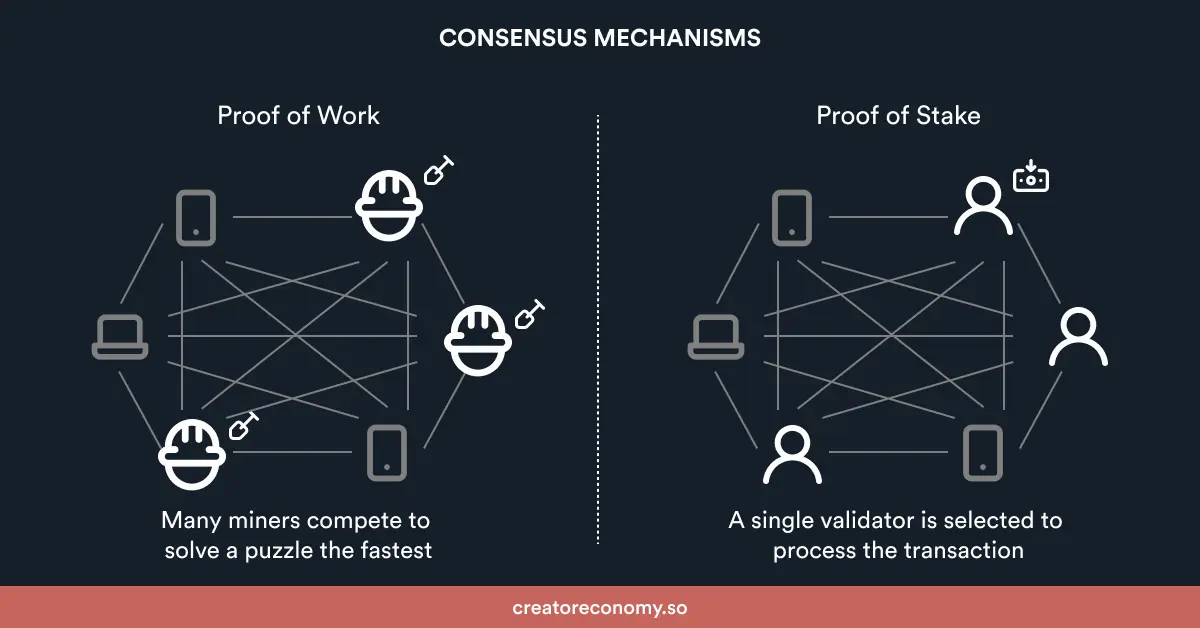
Photo: Consensus mechanisms, Source: creatoreconomy.so
In general, consensus is an agreement. In blockchain, it’s an agreement about the present state of the data in the network.
A consensus mechanism is a protocol that provides reliability and trust in the blockchain network. It brings all nodes in the blockchain to agree on a single data set, verify transactions, and keep the network secure.
While there are many different consensus mechanisms, the most widely used are Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS). To learn more about consensus mechanisms on Solana, check out our blog for Proof of History and Proof of Stake.
3. Cryptographic Hash Functions
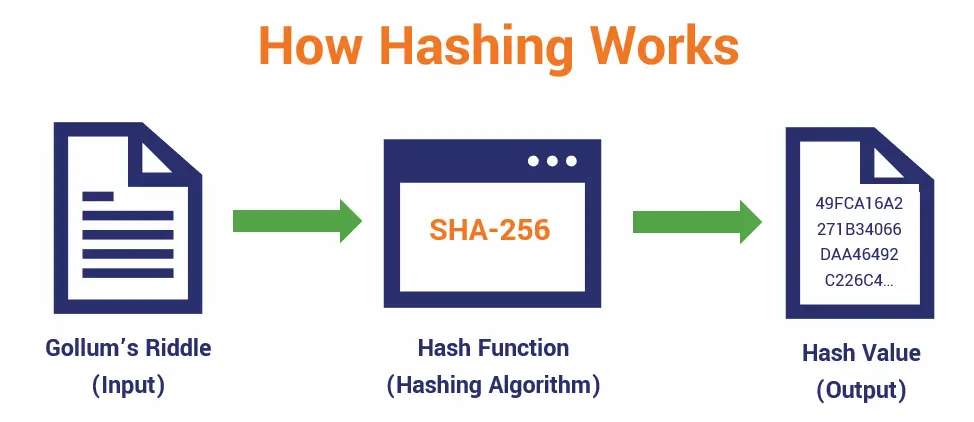
Photo: How hashing function works, Source: cyberhoot.com
Of course, something has to connect the blocks in a chain. That’s where the cryptographic hash functions come into play!
Basically, it’s a mathematical function that takes an input value and compresses it into a hash, a random numerical value. Hash is always a fixed length.
Because the hash is random and unrelated to the original input, it secures the message block and ensures data integrity. It’s crucial for data storage and authentication.
4. Smart Contracts
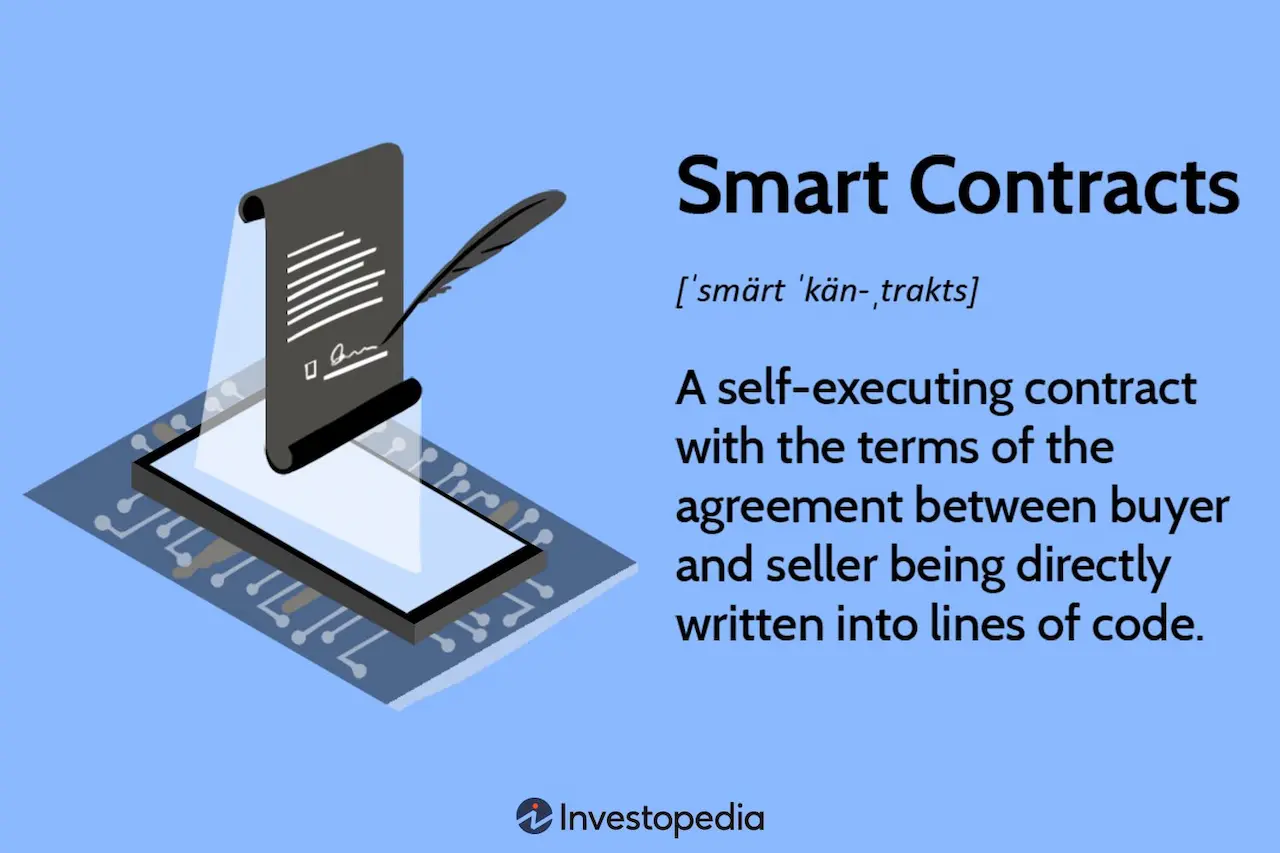
Photo: Smart contracts, Source: investopedia.com
Smart contracts are self-executing digital scripts. They automatically execute when the predetermined terms and conditions are met.
It’s important to note that they consist of any legal language, terms, or agreements, only code. After they are completed, the transactions are trackable and irreversible.
5. Public and Private Keys
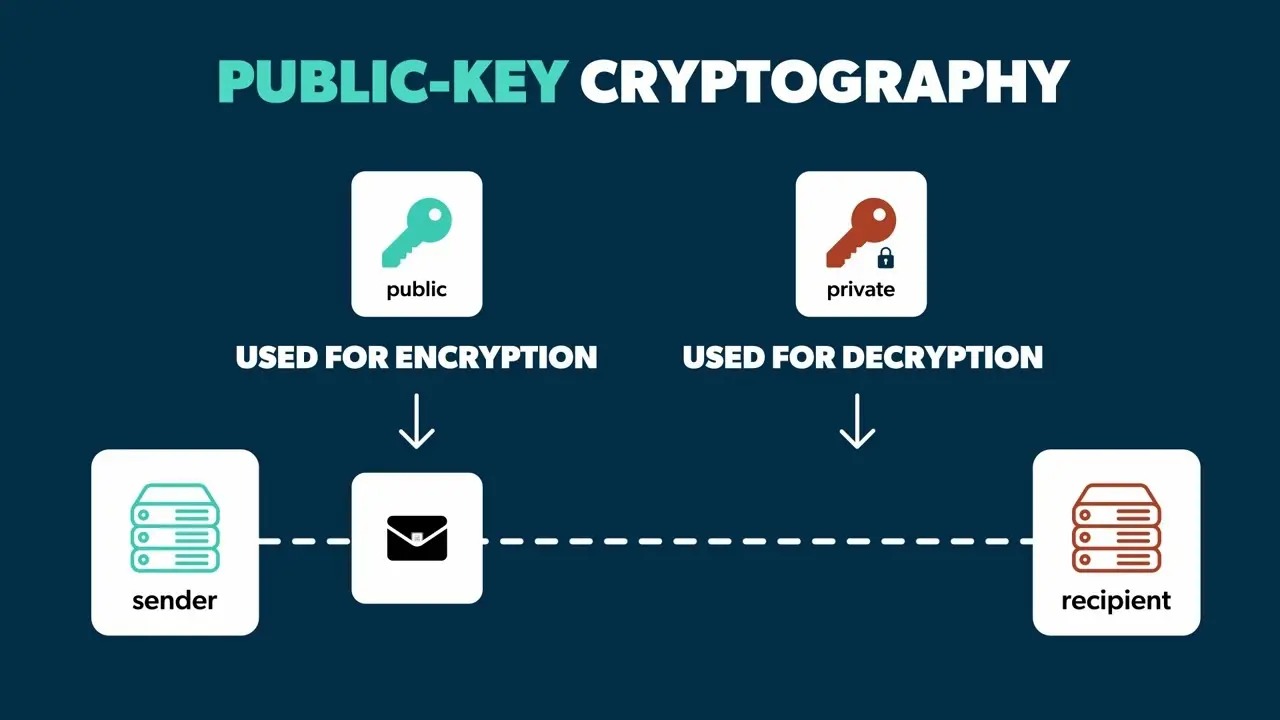
Photo: Public-key cryptography, Source: JumpCloud on YouTube.com
To secure transactions, blockchain uses public-key cryptography. Each participant has a pair of cryptographic keys.
The public key serves as an address for receiving funds. Contrarily, the private key is kept secret, it’s used for signing transactions.
6. Tokenization
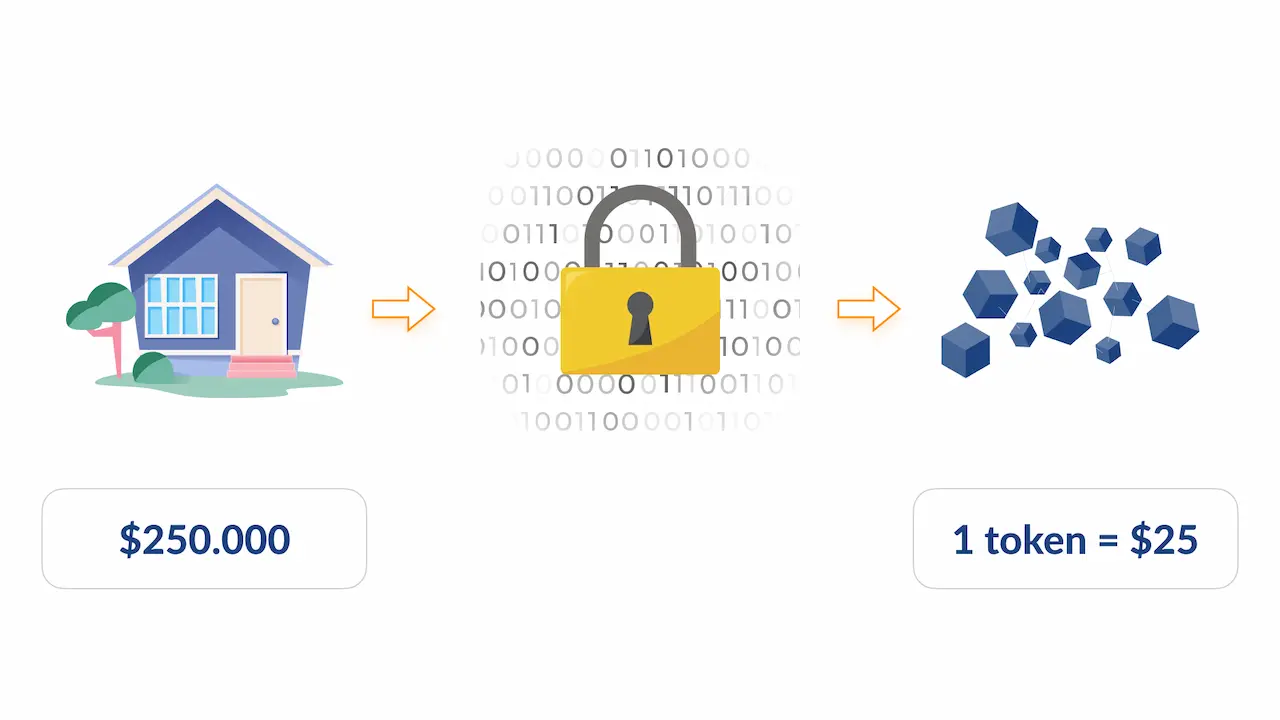
Photo: Tokenization on the blockchain, Source: blog.omertex.com
Generally, tokenization is a digital, unique, and anonymous representation of real assets. We use it daily to secure sensitive data such as payment information.
In blockchain, tokens can take many forms, from representing a store of value to digital or even real-world assets. Essentially, tokenization is creating digital tokens from these real things to use them on the blockchain.
Final thoughts
Finally, you are familiar with the most fundamental concepts behind blockchain technology, the backbone of cryptocurrency systems and the Web3.
While there is so much more yet to learn about blockchain, knowing these concepts helps you understand how blockchain stays secure, transparent, and trustworthy.
We aim to educate you about each of these so keep reading our blog to master the technical side of crypto!
Let us help you safely launch your NFT project