Solana's Consensus Mechanisms: Proof of History PoH) & Proof of Stake (PoS)

As you learn about Crypto, you will hear about Proof of History (PoH), Proof of Stake (PoS), and other protocols.
While new investors may consider this too complex to understand, these protocols are essential for cryptocurrencies. After all, they are the reason why crypto can stay decentralized. They verify transactions without third parties.
So, the more you know about PoH and PoS, the better!
This guide explains how Solana’s consensus mechanisms work. First, there’s a simplified overview. After you’ve mastered the basics, we will step into a more technical description. Read this guide and start making more informed decisions!
Solana Proofs
Perhaps you have heard of Bitcoin’s Proof of Work (PoW) consensus mechanism. There, miners use computational power. In contrast, Solana secures its network with Proof of Stake (PoS) and Proof of History (PoH) to facilitate faster transactions and lower fees.
The PoS and Poh simply stake SOL tokens and allow validators to keep Solana running asynchronously.
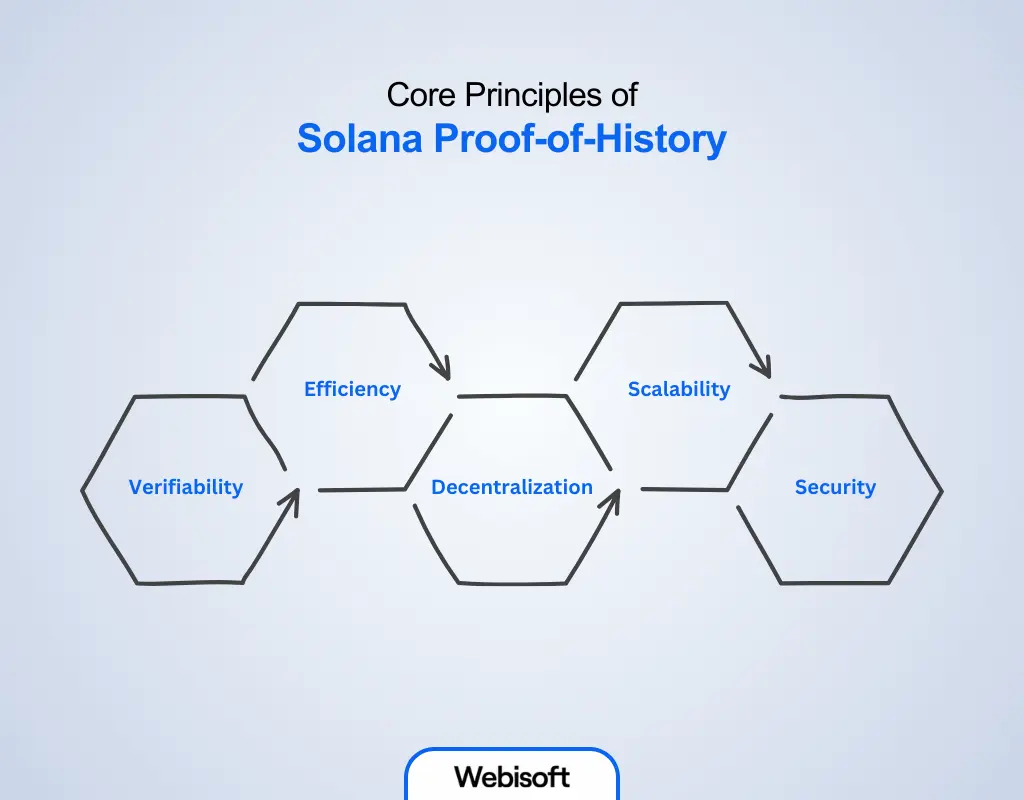
Photo: Core Principles of Solana Proof-of-History, Source: webisoft.com
Let’s learn more about each of them and how they work together to achieve high throughput!
What is Proof of History (PoH)

Photo: Proof of History, Source: chaindebrief.com
Proof of History is a consensus mechanism that Solana uses. In fact, Solana is the world’s first blockchain to use PoH. Alongside Proof of Stake, PoH solves the issue of universal blockchain time and increases the network speed.
Concept of a Cryptographic Clock
Simply explained, PoH is a way to keep the time between computers that don’t trust each other. Instead of depending on communication between nodes to agree on the time and sequence of events, each node creates a record proving that events have occurred at a specific moment in time.
We can visualize it as a photographer taking a series of photos with timestamps. You can see the order in which the events occurred. There's no need to ask everyone to agree on the time they were taken.
One of Solana’s main advantages is its high efficiency in processing transactions. Thanks to PoH, it’s faster compared to Bitcoin or Ethereum.
What is Proof of Stake (PoS)

Photo: Proof of Stake, Source: investopedia.com
Proof of Stake (PoS) is another consensus mechanism. Blockchains use it for processing transactions and creating new blocks. While Ethereum and Bitcoin use Proof of Work (PoW), PoS is the alternative used to validate transactions on Solana.
The main difference is that PoS doesn’t require as much energy to validate blocks as PoW does. The reason is that stakers don’t use mining to solve energy-intensive crypto problems. Instead, they use smart contracts to lock funds.
Moreover, PoS is more scalable because it allows more transactions per second.
Validator Participation
Solana uses the traditional PoS model. Validators stake their SOL tokens as collateral to vouch for the accuracy of the blocks they validate.
Based on the size of their stake, validators are chosen to write new blocks. They are rewarded with transaction fees and block rewards in proportion to their stakes.
Technical Explanations of PoH and PoS
So, it’s time to dive into the more complex, technical side of Solana’s consensus mechanism.
How Proof of History Works
First, let's briefly explain node since we've already mentioned it. Node is a computer connected to other computers, which shares information and follows a set of rules.
With Proof of History, nodes have their internal clock. It verifies events and the passage of time. Nodes can look at the sequence of incoming events and tell their order without validating time with other nodes.
Although it seems complicated at first, in a nutshell, PoH makes transactions on Solana faster.
Sequence Hashing
Proof of History works by having a verifiable sequence of hashed events. In essence, blocks on Solana are signed by a single-core Verifiable Delay Function (VDF). This executing function simply takes a previous output and generates a new one at fixed intervals. Thus, each output becomes a unique historical record.
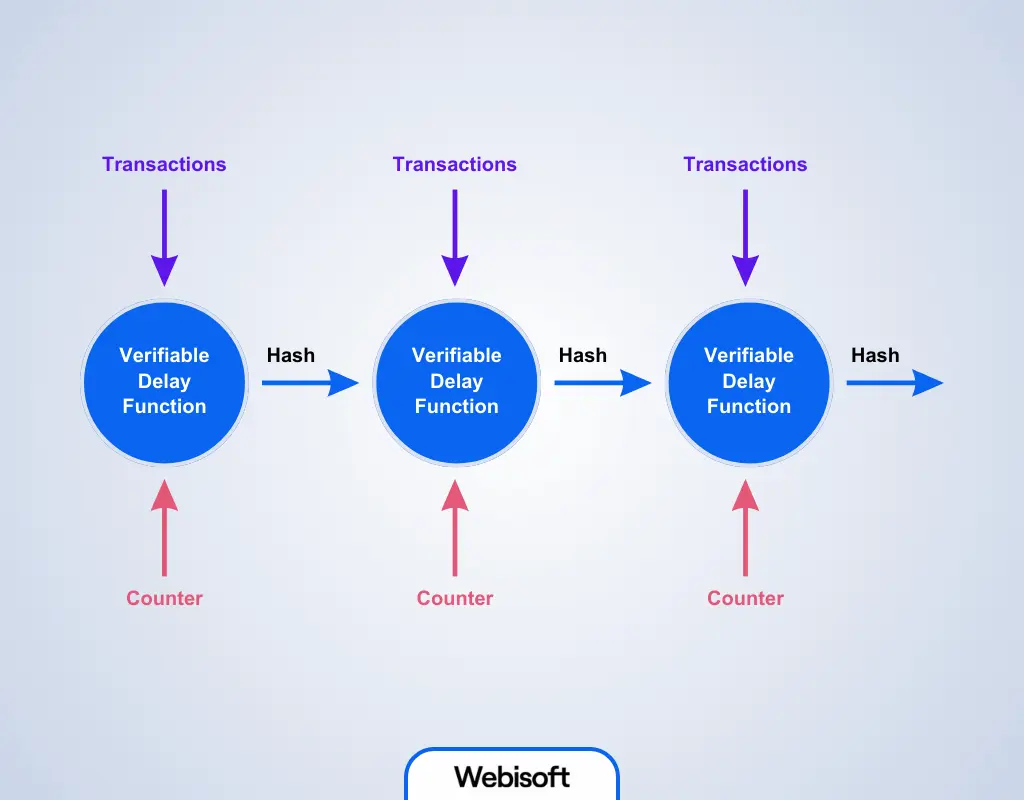
Photo: How Does PoH work with PoS, Source: webisoft.com
Hash Chain Linkage
As can be seen in the image, functions are chained together. One function’s output is another function’s input. Each new hash incorporates the one before it and some data (like a transaction), which timestamps this data. This sequence forms a historical record, proving data existed when it entered the hash chain.
How Proof of Stake Works
With Proof of Stake, stakers are like crypto miners. However, stakers lock up their cryptocurrency to act as validator nodes. The amount of crypto you hold and stake will determine the chance of you validating a block.
The more you stake, the higher the chances of you validating new blocks and earning rewards.
Validator Election
Validators are periodically elected as leaders. Then, they get the right to propose the next block in the chain. This is based on the size of their stakes.
Block Proposal
The elected leader aggregates transactions into a block and uses PoH to timestamp them. Then, the leader broadcasts this proposed block to other validators.
Voting and Finalization
Other validators verify the block’s PoH sequence and transactions. If the majority agrees it’s valid, the block is added to the blockchain. Remember, the voting process depends on their stakes.
How PoH and PoS Work Together
So, how do PoH and PoS work together to achieve high throughput?
Proof of History addresses timing and speed. It provides a way to verify the order and timing of transactions independently and quickly.
Meanwhile, Proof of Stake secures the network. Basically, PoS ensures that validators have something (their SOL tokens) at risk while participating in network governance and block production. This solves the problem of choosing a validator and penalizing malicious validators.
Gulf Stream
Solana uses Gulf Stream, a mempool-less transaction forwarding protocol. It pushes transactions to the network’s edge, closest to the current block leader. This gives the leader faster access to transactions and reduces confirmation time.
Fork Choice
Solana employs a Tower BFT, a PoS-based version of the practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (pBFT) consensus algorithm. It weights votes according to the stake and incorporates the history PoH provides. In other words, this algorithm helps with the validator consensus and fork resolution.
Final thoughts
Finally, now PoS and PoH may sound more than just crypto jargon. As you get more familiar with them, you will gain a higher understanding of how Solana revolutionized the way blockchains work.
While Proof of History may be new and still somewhat unproven, it helps establish the truth about the order and timing of events. The result is an increased transaction speed, improved scalability, and energy efficiency.
This historical truth, combined with the security of Proof of Stake, where validators risk their assets to validate transactions, ensures Solana is a secure and reliable blockchain network. Hopefully, now you have a better understanding of Solana's proofs. To continue learning about Solana and web3, read other Iron Node blogs. Make sure to check out our beginner's guide to fundamental blockchain concepts!
Let us help you safely launch your NFT project